Listen here on Spotify | Listen here on Apple Podcast
Episode released on March 20, 2025
Episode recorded on October 28, 2024
 Gordon Wells is the Program Manager for MAGIC at the University of Texas at Austin Center for Space Research and serves on the State Governor’s Emergency Management Council.
Gordon Wells is the Program Manager for MAGIC at the University of Texas at Austin Center for Space Research and serves on the State Governor’s Emergency Management Council.
Highlights | Transcript
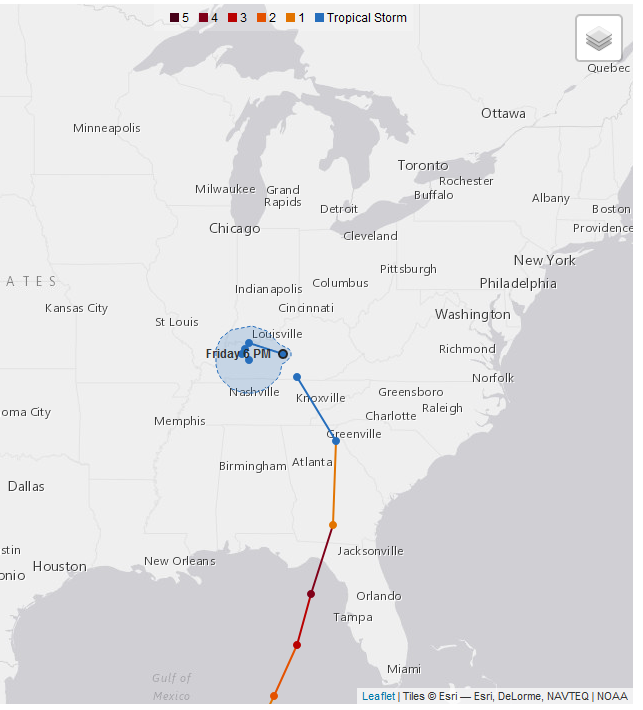
- Hurricane Helene made landfall on Sep. 26 (2024) as a Category 4 Hurricane in Big Bend region of Florida, near city of Perry and dissipated on Sep. 29 (Fig. 1). Fatalities totaled ~ 230 across Fl, GA, SC, NC, TN, and VA. Storm surge was ≤ 16 ft with lot of wind and water damage, predicted using the Advanced Circulation (ADCIRC) model by Clint Dawson and his team. ADCIRC results are provided to the public through the CERA (Coastal Emergency Risks Assessment) website (Dr. Carola Kaiser, LSU).
- Helene blended with a front in N Carolina and N Georgia to generate intense heavy rain.
- Gordon Wells and his team provide information to field teams on location and timing of the storm to optimize their work.
- His team also supports teams who are deployed out of state upon request. One example is the Texas A&M Task Force 1 (TX-TF1), 1 of 28 urban search and rescue teams under the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
- Gordon’s team supports these groups with predictive services, such as storm surge, wind, or wave action based on satellite telemetry, and data analytics to provide imagery on storm location and severity.
- Gordon works out of the State Operations Center in Austin and uses satellite data from NOAA, NASA, Dept. of Defense, and FEMA. In addition, they have access to ~40 Intl. Space Agency Platforms through the International Charter Space and Major Disasters. They also include data from airborne sensors.
- Data are streamed to the Univ. of Texas Center for Space Research. Gordon works with coordinators from 32 state and 8 Federal Agencies in the State Operations Center. Gordon and his team customize data to respond to requests.
- Hurricane Helene: National Hurricane Center (NHC) uses global models (Global Forecast System, GFS) with embedded hurricanes and underpredicted the severity of Hurricane Helene (CAT 1 at landfall). Hurricane specific models (e.g., Hurricane Analysis and Forecast System, HAFS) were much more reliable for Hurricane Helene. Need to adapt in response to uncertainties in forecasting.
- Storm surge from hurricane pushes water inland, precludes tributaries from exiting, creating backwater.
- Compound flooding includes storm surge near the coast and inland flooding from pluvial (rainfall) and fluvial (riverine) flooding.
- Hurricane winds move counterclockwise, transporting water away from the coast in some regions and inland in other regions.
- Hurricane Milton: storm trajectory going to push water into Tampa Bay; however, track moved southward and E and NE winds moved water out of Tampa Bay, negative storm surge (NYT link).
- Hurricane Harvey, 2017, Gordon in State Operations Center, Harvey, indefinite storm track, landfall Coastal Bend near Corpus Christi, storm surge, wind damage in coastal barriers and port areas.
- Heavy rainfall moved eastward, maximum rains in Beaumont and Port Arthur Texas.
- Maximum rainfall > 60 inches over Nederland (N of Port Arthur), moving slowly, 3 d landfall to move across TX and into LA.
- Gordon works with many agencies: Dept. Transportation, ERCOT (electricity), water treatment plants, and the Red Cross.
- Airborne data show whether the Red Cross deliveries reach points of distribution (PODs). Aircraft from National Guard.
- Thermal imagery and radar satellites are effective for nighttime coverage.
- NASA flew instruments on aircraft at ~ 12 km (41,000 ft) during Harvey that will be on the NASA Indian Space Research Organization satellite (NASA ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, NISAR) over flooded river basins. NISAR is projected to be launched in March 2025.
- Many rural communities had more damage from Harvey than metropolitan Houston on a per capita basis.
- Recovery from Harvey: Harris County Flood Control Districtbuy back homes, retrofitting and weatherizing electricity systems, and elevating properties. The Baker Institute evaluated Houston’s flood vulnerability six years after Hurricane Harvey .
- What level of storm should you prepare for in future?
- Drought:
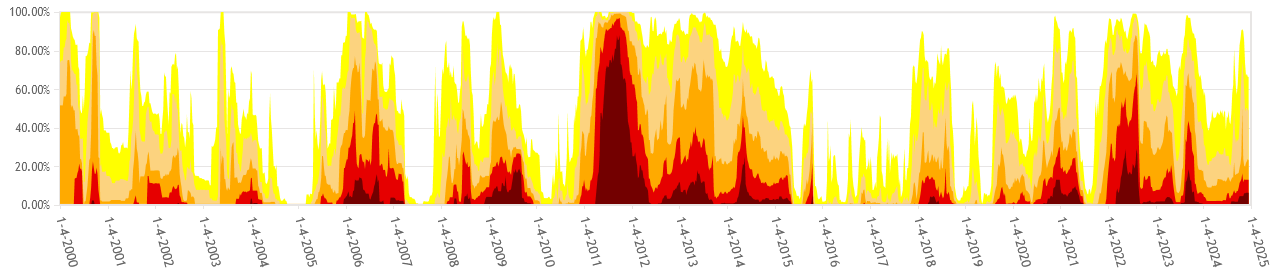
- Often drought in some parts of TX and flooding in other parts.
- Gordon serves on Drought Preparedness Council which includes the state climatologist (John Nielsen Gammon), state agencies, academics etc.
- Assess what groundwater wells might dry up, 180 days before running out of water (drilling emergency well or transporting water in tanks)
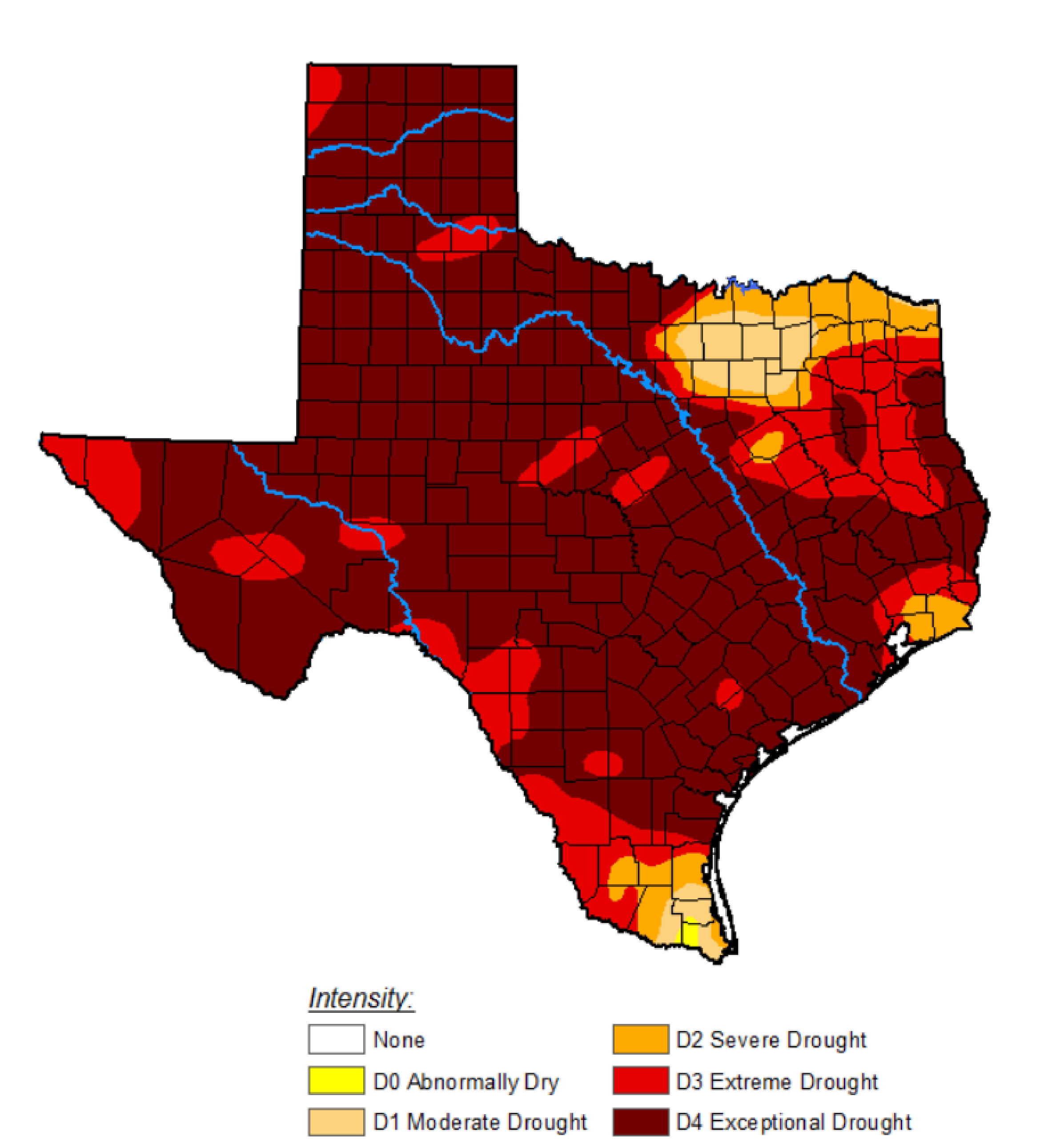
- Major drought in TX: 1950 – 1957, 2011 exceptional drought (US Drought Monitor, TWDB Monitor) (Figs. 3, 4).
- Long term drought 2011 – 2013 -2014 followed by flooding in Trinity River Basin, Wimberley, Texas (Fig. 4).
- Memorial Day floods May 31 2015.
- GRACE satellite data, water loss from State 2011 – 2014; water gain during wet period: 2015 – 2017.
- Water loss during drought: equivalent to ~ 3 entire Lake Meads (36 km3 capacity) in Texas.
- NASA Terra and Aqua MODIS satellites and VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) sensor track vegetation changes related to droughts and floods, NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index.
- Wet periods; build up vegetation biomass, provide fuel for wildfires during droughts.
- Austin ranked 5th in terms of cities vulnerable to wildfires in the US (CoreLogic).
- Natural vegetation in Austin area before human habitation was prairie woodland.
- Humans have been suppressing wildfires; therefore, fuel load building up.
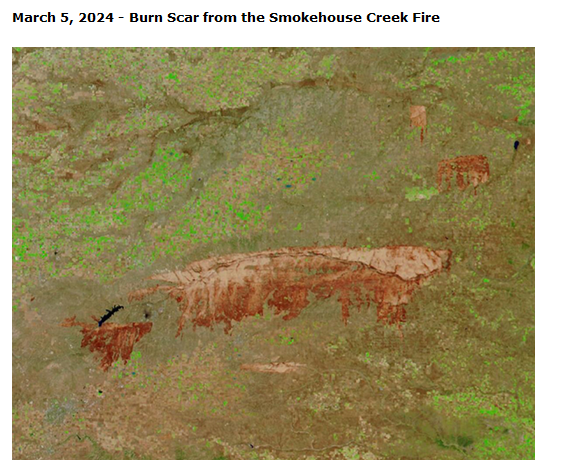
- Smokehouse Creek Fire: N of Amarillo (Texas Tribune, Mar 16, 2024), forecasted by TX A&M Forest Service maximum day and geography well, high winds and extremely low RH after wet period preceding year (spring and summer). Fire spread 100 miles in 30 hr.
- Thermal fire points from satellite data, optical imagery, see where it burned (Fig. 5).
- Could determine fire started along transmission corridor for electrical power, where old utility poles were blown over.
- Bastrop Fires: pine trees, unusual for Central TX, fire spread on the ground. Homes with wooden decks and built up pine needles were burned.
- TX is most disastrous state by economic impacts of disasters since 1980: tornadoes, severe storms, hail, drought, floods, hurricanes (National Center for Environmental Information, NCEI, Texas summary).
- Gordon collaborates with Japanese on technology to get real-time response during emergencies and build resilient disaster proof habitation.
- Federal and State programs to increase resilience to emergencies.
- Texas Integrated Flooding Framework (TIFF) funded by Texas General Land Office through the Texas Water Development Board.
- Booming population in Texas exacerbating vulnerability to disasters.
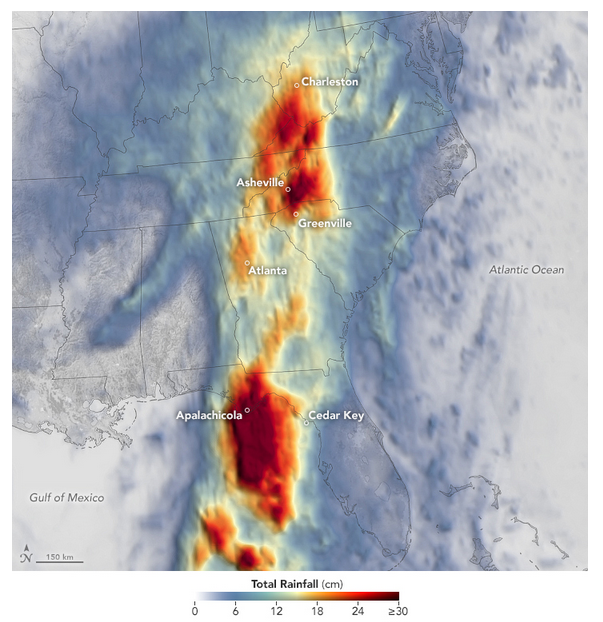
Up to 50 cm of rainfall occurred in the mountains of the Carolinas (link).